
Materials Chemistry Group
Functional (pharmaceutical) molecular solids
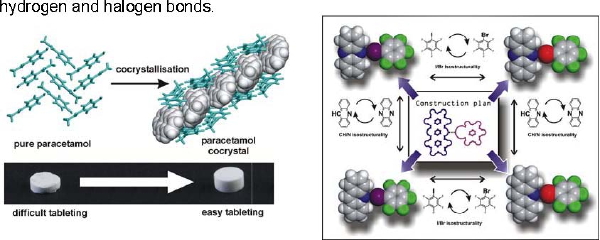
The design of functional molecular materials has advanced tremendously through cocrystallisation: the assembly of multiple chemical species in the same crystal lattice. Underlying cocrystals formation are rules that guide molecular recognition and self-assembly. We are deciphering this "intermolecular language" by combining experimental work with data mining and molecular modelling. Our particular interest is constructing functional materials through weak supramolecular interactions, such as hydrogen and halogen bonds.
Surface dynamics of molecular solids
Properties of crystalline solids are usually measured as a bulk property, and the results interpreted in terms of crystal structure. However, such a description does not adequately describe the surface of molecular crystals, at which the distribution of forces on a molecule is non-symmetrical, resulting in high mobility and reactivity. The atomic force microscope (AFM) is a unique tool for studying such surface-related dynamics.
Teaching
Current teaching includes a third year undergraduate lecture course on the Chemistry of Materials. The course examines a range of organic, metal-organic and inorganic materials and demonstrates their varied uses. We will, in particular, identify important structural features relevant to such areas as the pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries and to naturally occurring biomaterials such as bone. The underlying chemistry and properties will be shown to be often sensitive to the way that the constituent atoms and molecules are packed together. This aspect of solid state control will be examined in some detail.
The development and design of new materials, incorporating structural characteristics of inorganic solids and functionality of organic molecules will be described.
The control of crystal morphology is important in many applications, and this will be discussed in the context of templating crystal growth, both in Nature and in the laboratory, and of crystal engineering. Numerous important materials, including many found in Nature, are in fact inorganic-organic composites, and these will also be discussed in detail.
From paracetamol to petrol to proteins to bone – the importance of the Chemistry of Materials will be explored in these lectures.
Also, as part of the Cambridge fourth year program I teach a course on Organic Solids that builds on the lecture course Chemistry of Materials given in Part II (although it is not required that students have taken this course). The first six lectures of the course, given by me, will cover aspects of crystal chemistry, structure and reactivity of organic solids. Examples of lattice controlled reactions will be given, including photochemical and thermal. Particular emphasis will be placed on how solid state properties impact on the development of drug products in the pharmaceutical industry. Experimental approaches to understanding molecular packing will be described and will lead into the second part of the course, given by my colleague, Dr Graeme Day.
Publications
- ‹ previous
- Page 24

