
Herchel Smith Professor of Medicinal Chemistry
Nucleic acids are fundamental to life. Our research is focused on the chemical biology of nucleic acids, and employs the principles of chemistry and the molecular sciences to address questions of importance in biology and medicine. Projects are inherently interdisciplinary and will provide scope for a diversity of intellectual and experimental approaches that include: organic synthesis, biophysics, molecular and cellular biology and genomics. Our scientific goals are problem-driven, which constantly raises the need to invent new methodology.
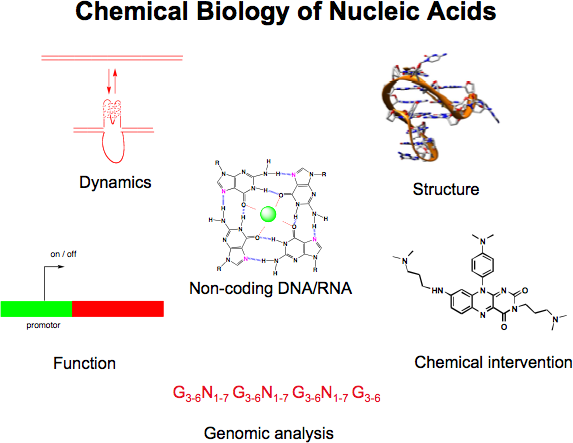
A major interest is to elucidate and manipulate mechanisms that control the expression of genes (either transcription, or translation). We are particularly interested in the role of non-canonical nucleic acid structures that control gene expression (e.g. G-quadruplexes, micro RNA and RNA structures in the 5' untranslated regions of mRNAs). Our goal is to design and synthesise small organic molecules that target such structures and alter the expression of certain genes of interest. Such small molecule gene regulators are valuable tools to study mechanisms in biology and will also open up new approaches for therapeutics and molecular medicine, particularly for diseases characterized by aberrant expression of certain genes (e.g. various cancers).
Our fundamental science will inevitably create opportunities for translation and commercialisation. One such example was our invention (with Professor David Klenerman) of new DNA sequencing technology ("Solexa sequencing") that was commercialised as a Cambridge University spinout company (now part of Illumina Inc.) and is used routinely for applications in genomics, including human genome sequencing.
Hear Shankar Balasubramanian discuss some of the group's research.
Watch Professor Balasubramanian discuss his research
Take a tour of the Balasubramanian Lab
Publications
- ‹ previous
- Page 12

