
What we do...
Our experimental work focuses on light-based sensing technologies which have applications in healthcare diagnostics, environmental monitoring and homeland security. We also use light-based techniques to analyse painted art-works without damaging them. In our computational work, we employ advanced computer-modelling techniques to 'design' and understand the physical behaviour of functional materials, such as new computer-memory materials.
We are funded by...
We are grateful to NIHR (i4i) and EPSRC for funding these projects.
Our research
Our research is mainly concerned with different aspects of (bio)chemical sensing (e.g. using MEMS or optical devices), and with non-crystalline materials (e.g. glasses), understanding their physical properties in terms of their atomic structure and defects. The approach is multidisciplinary, covering solid-state chemistry, physics and materials science. Areas of interest include:
- Microcantilever sensors for ultra-sensitive detection of chemical and biological analytes.
- Optical sensors, including evanescent-waveguide sensors, SERS using holographic substrates.
- Computer simulation of the atomic structure and vibrational dynamics of disordered materials.
- Ab-initio computer simulation of phase transformations and optically-induced metastabilities in glasses, e.g. used in phase-change memories (Flash replacement).
- Experimental study of optically-induced changes in glasses, with applications in the fields of optical- waveguides and chemical sensors, data storage and all-optical actuation.
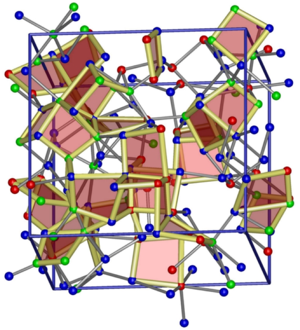
Figure: Ab initio molecular-dynamics model of the amorphous state of the phase-change non- volatile memory material Ge2Sb2Te5
Selected Publications
- Computer-simulation design of new phase-change memory materials. Phys. Status Solidi A 207, 510 (2010)
- Spatial distribution of rare-earth ions and GaS4 tetrahedra in chalcogenide glasses studied via laser spectroscopy and ab initio molecular dynamics simulation. Phys. Rev. B 81, 104204 (2010)
- Simultaneous readout of multiple microcantilever arrays with phase-shifting interferometric microscopy (PSIM) Rev. Sci. Instr. (2009), 80, 093101-8
- Evidence of formation of tightly bound rare-earth clusters in chalcogenide glasses and their evolution with glass compositions. Phys Rev B, (2009), 79, 180202(1-4)
- Evanescent-Wave Excitation of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Substrates by an Optical-Fiber Taper. Optics Letters (2009) 34, 2685-2687
- Microscopic origin of the fast crystallization ability of Ge-Sb-Te phase-change memory materials, Nat. Mat., (2008), 7, 399
- All-optical actuation of amorphous chalcogenide-coated cantilevers, J. Non-Cryst. Sol., (2007), 353, 250.
- Universal features of terahertz absorption in disordered materials, Phys. Rev. Lett., (2006), 97, 055504
- Universal features of localized eigenstates in disordered systems, J. Phys. Cond. Matt, (2005), 17, L321
Publications
- ‹ previous
- Page 19

