
University Associate Professor
Our research is focused on the synthesis and characterisation of new materials, primarily using solvothermal synthesis. In this technique, reactions occur in solvents at temperatures above their normal boiling points by containing the reaction mixture within a pressure vessel. We have found this method to be particularly good for preparing porous materials for hydrogen storage and gas separation as well as new magnetic materials. We have an extensive range of collaborations with groups in the UK, the rest of Europe and in South Korea for performing measurements on the magnetism and porosity of our compounds.
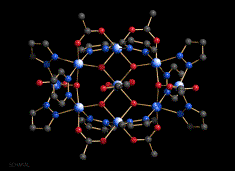
- Magnetic materials are being prepared as part of the search for 'single molecule magnets' which represent the ultimate in magnetic data storage efficiency. We are also preparing compounds with which physicists can test theoretical models of magnetic behaviour; the same theories can be applied to other types of symmetry breaking in areas as diverse as protein folding and the early universe.
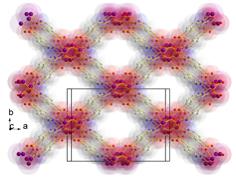
- New porous materials are much sought-after for gas storage in a future hydrogen economy. This is a very active area of research as zero-emission fuel sources are very attractive. Such materials could also be used as size- and shape-selective catalysis as well as gas separation and materials. The 'metal-organic framework' materials prepared in our lab are some of the most efficient hydrogen storage materials yet measured.
Publications
Gas-sorption selectivity of CUK-1: A porous coordination solid made of cobalt(II) and pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid
Advanced Materials
(2007)
19
1830
(doi: 10.1002/adma.200601983)
Porous cobalt(II)-organic frameworks with corrugated walls: Structurally robust gas-sorption materials.
Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English)
(2006)
46
272
(doi: 10.1002/anie.200601627)
Static and dynamic properties of Mn-2(OH)(2)(C4O4)
Physica B Condensed Matter
(2006)
385
435
(doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2006.05.144)
Order-disorder transition in monoclinic sulfur: a precise structural study by high-resolution neutron powder diffraction.
Acta crystallographica. Section B, Structural science
(2006)
62
953
(doi: 10.1107/S0108768106039309)
New phosphorus-selenium heterocycles
Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Silicon and the Related Elements
(2006)
41
51
(doi: 10.1080/10426508908039691)
Structural and magnetic studies of the tris(cyclopentadienyl)manganese(II) "paddle-wheel" anions [Cp(3-n)(MeCp)(n)Mn](-) (n=0-3, MeCp=C(5)H(4)CH(3), Cp=C(5)H(5)).
Chemistry A European Journal
(2006)
12
3053
(doi: 10.1002/chem.200501214)
A new Co(II) coordination solid with mixed oxygen, carboxylate, pyridine and thiolate donors exhibiting canted antiferromagnetism with TC≈68K
Chem Commun (Camb)
(2006)
1607
(doi: 10.1038/600347h)
Compounds with the “Maple Leaf” Lattice: Synthesis, Structure, and Magnetism of Mx[Fe(O2CCH2)2NCH2PO3]6⋅n H2O
Angewandte Chemie International Edition
(2006)
45
803
(doi: 10.1002/anie.200502847)
Isolated Magnetic Clusters of Co(II) and Ni(II) within 3-Dimensional Organic Frameworks of 6-Mercaptonicotinic Acid: Unique Structural Topologies Based on Selectivity for Hard and Soft Coordination Environments
Inorganic chemistry
(2005)
44
5981
(doi: 10.1021/ic050768q)
Possible strong symmetric hydrogen bonding in disodium trihydrogen bis( 2,2′-oxydiacetate) nitrate
Acta Crystallographica Section E: Crystallographic Communications
(2005)
61
m1174
(doi: 10.1107/s1600536805014819)
- ‹ previous
- Page 4

