
Professor of Theoretical Chemistry
What we do...
Our theoretical research group uses mathematical and computational techniques to investigate quantum behaviour in the motion of atomic nuclei. We carry out computer simulations which illustrate how quantum mechanics changes the motion of atoms and molecules in chemical reactions and inside liquid water and ice.
Research
Our research investigates how the quantum properties of atomic nuclei affect chemical reaction rates and mechanisms. We develop and apply a wide range of theories and computational techniques, from exact solutions of the Schrödinger equation for small systems, to approximate Feynman path- integral approaches for larger systems.
First-principles calculations of wave functions of chemical reactions
We were the first group to calculate a complete time-dependent wave function that visualizes the entire dynamics of a chemical reaction from approach of the reactants through to scattering of the products into space. This work is done in collaboration with a leading experimental group (R.N. Zare, Stanford) who measure detailed product-scattering patterns that our calculations reproduce and interpret in terms of first-principles quantum mechanics.
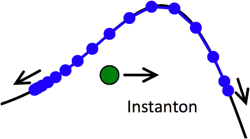
Instanton simulations of quantum tunnelling
Instantons arise when Feynman path-integral theory is used to describe quantum tunnelling through barriers; they describe the dominant tunnelling path, which gives an approximate but physically rigorous description of the tunnelling dynamics. We have recently developed and extended instanton theory such that the instantons are represented by a series of beads which can be rapidly strung together to describe quantum tunnelling in complex systems. We are currently applying this method to tunnelling in water clusters (in collaboration with Prof. D.J. Wales), and to proton transfer reactions in solution.
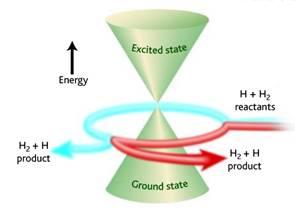
Winding effects at conical intersections
Conical intersections arise when potential energy surfaces intersect. We have found that the nuclear wave functions at such intersections can be unwound, such that contributions from Feynman paths that wind different numbers of times around the intersection can be rigorously separated. This gives rise to quantum interference effects; we are currently investigating how such effects influence the efficiency of relaxation through a conical intersection.
Publications
- ‹ previous
- Page 8

