
University Associate Professor
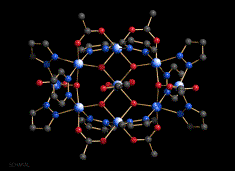
Our research is focused on the synthesis and characterisation of new materials, primarily using solvothermal synthesis. In this technique, reactions occur in solvents at temperatures above their normal boiling points by containing the reaction mixture within a pressure vessel. We have found this method to be particularly good for preparing porous materials for hydrogen storage and gas separation as well as new magnetic materials. We have an extensive range of collaborations with groups in the UK, the rest of Europe and in South Korea for performing measurements on the magnetism and porosity of our compounds.
- Magnetic materials are being prepared as part of the search for 'single molecule magnets' which represent the ultimate in magnetic data storage efficiency. We are also preparing compounds with which physicists can test theoretical models of magnetic behaviour; the same theories can be applied to other types of symmetry breaking in areas as diverse as protein folding and the early universe.
- New porous materials are much sought-after for gas storage in a future hydrogen economy. This is a very active area of research as zero-emission fuel sources are very attractive. Such materials could also be used as size- and shape-selective catalysis as well as gas separation and materials. The 'metal-organic framework' materials prepared in our lab are some of the most efficient hydrogen storage materials yet measured.
Publications
Muonium addition to sulfur-nitrogen chains
Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry
(2000)
38
S65
Large metal clusters and lattices with analogues to biology
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences
(1999)
357
3099
(doi: 10.1098/rsta.1999.0483)
Synthesis and Structures of Organometallic Aqua Complexes of Ruthenium(II)
Organometallics
(1999)
18
4068
(doi: 10.1021/om990411s)
New type of metal squarates. Magnetic and multi-temperature X-ray study of di-hydroxy(µ 6 -squarato)manganese†
Chemical Communications
(1999)
1561
(doi: 10.1039/a903032h)
Hydrothermal crystallisation and X-ray structure of anhydrous strontium oxalate
Polyhedron
(1999)
18
2499
Solvothermal synthesis of the canted antiferromagnet {K2[CoO3PCH2N(CH2CO2)2]}6•xH2O
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
(1999)
38
1088
Formation and X-ray structure of a novel water-soluble tertiary-secondary phosphine complex of ruthenium(II): [Ru{P(CH2OH)3}2{P(CH2OH) 2H}2Cl2]
Chemical Communications
(1998)
1107
(doi: 10.1039/a801546e)
Biomimetic control of iron oxide and hydroxide phases in the iron oxalate system*
Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions
(1997)
4061
(doi: 10.1039/a704400c)
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel One-Dimensional Phases from Supercritical Ammonia: Cs3Ag2Sb3S8, α- and β-Cs2AgSbS4, and Cs2AgAsS4
Chemistry of Materials
(1996)
8
721
(doi: 10.1021/cm950392m)
Supercritical ammonia synthesis and characterization of four new alkali metal silver antimony sulfides: MAg2SbS4 and M2AgSbS4 (M = K, Rb)
Journal of Solid State Chemistry
(1996)
123
277
(doi: 10.1006/jssc.1996.0179)
- ‹ previous
- Page 8

