
Professor of Chemical Physics
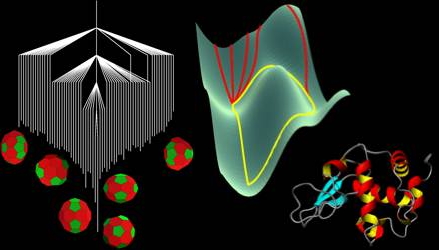
The self-assembly of complex mesoscopic structures, the folding of proteins, and the complicated phenomenology of glasses are all manifestations of the underlying potential energy surface (PES). In each of these fields related ideas have emerged to explain and predict chemical and physical properties in terms of the PES. In studies of clusters and glasses the PES itself is often investigated directly, whereas for proteins and other biomolecules it is also common to define free energy surfaces, as the figure below illustrates for lysozyme.
Applications of energy landscape theory in my group range from studies of tunnelling splitting patterns in small molecules to computer simulation of protein folding and misfolding, including aggregation of misfolded proteins. Other active research topics include global optimisation and investigation of how the thermodynamic and dynamic properties of glasses are related to the underlying PES.
Two recent advances are now providing new insight into larger systems. Discrete path sampling enables dynamical properties to be obtained efficiently, and is being used to calculate folding rates for proteins. Unexpected connections between dynamics and thermodynamics have also been revealed by the application of catastrophe theory to energy landscapes, and new results are now being obtained to characterize phase transitions.
Publications
- ‹ previous
- Page 22

